Marketing Attribution Models: Choosing the Right One
Read Time 6 Minutes
Marketing attribution models are a vital piece of any marketer’s strategy. Knowing where leads and conversions come from is information marketers simply can’t afford to do without. Getting comprehensive data on the steps in your buyer’s journey is key to increasing leads, proving ROI, driving revenue, and providing the best possible customer experiences. Marketing attribution models provide this.
Despite the variation of attribution models around, many marketers report gaps in data preventing accurate attribution.
Having accurate and comprehensive attribution data is crucial to many aspects of an organization’s success. Research shows that 64 percent of marketers report that data-driven strategies are essential to their success today. With so much riding on data, it makes sense to be sure you’re getting attribution data for all of your leads and conversions.
What is Marketing Attribution?
Marketing attribution is the process of giving credit for a lead or conversion to the advertising source that generated it. Why is it important that we ‘give credit’ to something? There are real dollars at stake for marketing teams. If you don’t know which marketing efforts are generating the activities you care about, you’re just guessing at the best way to allocate that money. With marketing teams often working with limited budgets, every penny needs to be spent in a way that makes an impact.
How is Attribution Determined?
Attribution models work differently when it comes to determining attribution. The classic models give credit to only one point whereas the multi-touch models give credit to different points along the journey. Some models are predetermined in where they give attribution but customized attribution models and data-driven attribution models allow for personalization based on your unique needs.
Today’s buyer’s journey is often complex and rarely linear. For marketers who want to maximize ROI, it’s vital to have insight into each step of the buyer’s journey. While it may be great that your top-of-funnel ad grabbed your lead’s attention, there’s often more to the story–and it pays to know.
For example, what happens if a customer first viewed a display ad, then a week later read one of your blogs, then a few days later clicked on a paid ad to do some additional research, before finally Googling your brand and making a purchase on your site? Which channel gets the credit for that revenue? The answer depends on the marketing attribution model you choose.
Marketing attribution models are sets of guidelines that determine the division of credit for each interaction your customer had on channels that led to a conversion or sale. In other words, marketing attribution models determine how much ‘credit’ each touchpoint in the buyer’s journey will get when someone becomes a customer or makes a purchase. Every buyer’s journey is unique, so marketers have developed multiple attribution models to account for these variations.

Types of Marketing Attribution Models
For many organizations, it makes sense to pay attention to the entire buyer’s journey and the touchpoints along the way. This is how you’ll find out which campaigns, ads, and channels are resonating the most with your target audience. When you know what’s working best, you’ll know where to focus more of your marketing efforts–and budget.
As mentioned, there are different types of marketing attribution models. It is important to take time to understand each of them and how they may align with your goals. Each model offers something different to meet marketers’ varying needs. At first, getting to understand the different types of models can be a lot. But, these models exist to be used by different organizations with different goals. And, there are times when you may use one model, and other times you’ll want to look at data from another one. Knowing your options is key to fine-tuning your attribution efforts.
The most common attribution models include:
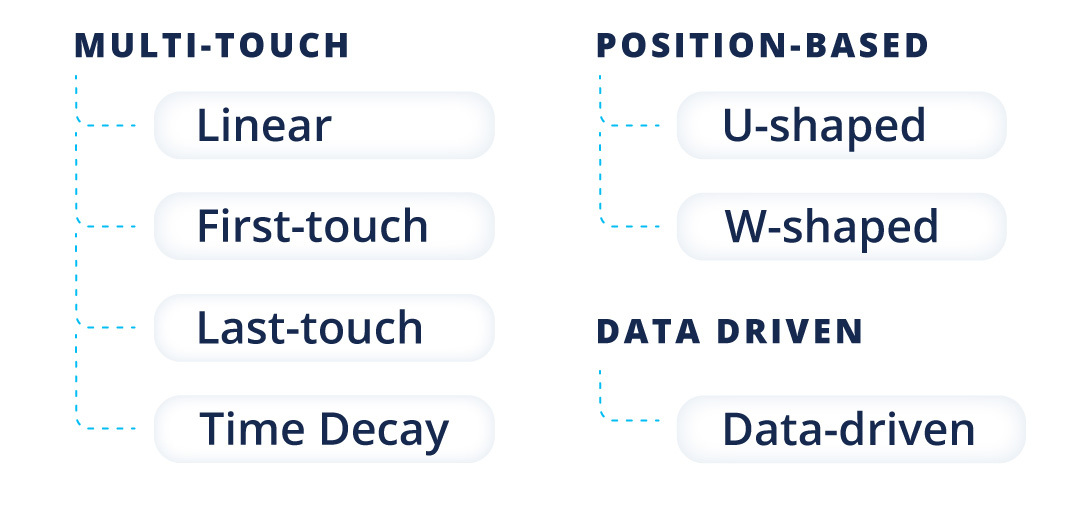
Classic Models for Marketing Attribution
First-touch
First-touch marketing attribution model gives 100% credit or ‘weight’ to the first customer touch point. As the name implies, the first click or impression is what’s counted in this model.
Use Case: While most marketers are looking for information about the full conversion path, there may be occasions when only the first touch needs to be considered. Organizations that are looking to understand the value of their top-of-funnel touchpoints or those with longer consideration periods may use the first-touch marketing attribution model.
Last-touch
Last-touch attribution gives 100% credit or weight to the last customer touchpoint. This marketing attribution model doesn’t take into account the first touchpoint or any of the interactions in between.
Use Case: This model gives marketers information about the last touchpoint on the customer’s conversion path or buyer’s journey. Organizations with short sales cycles or those wanting to evaluate the value of the bottom of the funnel campaigns may benefit from using the last-touch marketing attribution model.
First-touch and last-touch models are important because they show the value of what grabbed your lead’s attention or what converted them. However, today there are a lot of marketing channels and potential touchpoints added to the mix. From paid ads and emails to website pages and newsletters, there are multiple places buyers interact with your product or service before they decide to buy. Today’s buyer’s journey almost always involves multiple touchpoints and multi-touch marketing attribution models are for marketers who want to track and attribute all of these.
Multi-touch Marketing Attribution Models
Linear
The most basic of the multi-touch attribution models, linear attribution gives equal credit to each of the touchpoints from first to last and each point along the way.
Use Case: This attribution model gives you a full view of all touchpoints in your buyer’s journey. Start-up organizations or those just beginning with attribution may benefit from the insight of a linear attribution model to begin to get an understanding of their customer and the conversion path.
Time decay
Often used for B2Bs that have extended sales cycles, this multi-touch marketing attribution model gives more credit for touchpoints occurring closer to the final sale and less to those at the beginning of the buyer’s journey.
Use Case: This type of attribution model gives comprehensive insight into the full conversion path. This type of multi-touch attribution model can help you to understand the value of more than just one touchpoint as with the classic models. These multiple touchpoints may better illustrate how multiple ads and campaigns impact conversion.
Position-based (U-shaped, W-shaped, Z-Shaped)
These models divide the credit for each touchpoint based on where it happened in the customer journey. U-shaped attribution gives 40% credit to the first and last touchpoints and evenly distributes the remaining 20% between all the touchpoints in between.
W-shaped attribution gives 30% credit to the first and last touchpoints and the opportunity created while the remaining 10% is evenly distributed between the other touchpoints.
Z-shaped attribution models are used primarily by B2Bs. In this model, there are basically four touchpoints that equal credit (22.5%). These are first touch, MQL, SQL, and last touch. Additional touchpoints equally share 10% credit.
Use Case: The position-based models go beyond crediting each touchpoint evenly and aim to divide the credit at a more granular level with the first and last touchpoints given the most credit. For sales cycles that have multiple touchpoints in the conversion path, these models can help to better understand the value of each of these interactions.
Data-driven
Data-driven marketing attribution is a bit different than the other marketing attribution models. With data-driven attribution, platforms use data from your account and past buyer activity to determine how much credit to give each interaction on the conversion path.
Data-driven models are specific to each advertiser. With this marketing attribution model, the paths of prospects who converted are compared to the paths of those customers who didn’t convert. This enables patterns to be revealed in the ad interactions that lead to conversions.
Use Case: Data-driven marketing attribution lets you really get deep insight into where your customers are finding the most value in your ads and campaigns–and where they don’t. This type of attribution model is for those organizations who are knowledgeable about attribution and want to take it a step further.
Time decay, linear, position-based, and data-driven marketing attribution models all look at more than just one touch point. These multi-touch marketing attribution models provide a more complete picture than first or last-touch models. But, that doesn’t mean first and last can’t accurately reflect the results of your marketing efforts. That’s why it’s important to spend some time choosing a model that makes the most sense for your campaigns.
Custom Marketing Attribution Models
Choosing the right attribution model for your business is essential. Multi-touch models provide you with information on the entire conversion path. In addition to the models mentioned, there are also custom marketing attribution models. With these types of models and the granular insight they provide, agencies and organizations can craft the perfect model and uncover what’s driving the ideal conversion.
In addition to this vital benefit, multi-touch marketing attribution models let you:
- Stop guessing which ads, campaigns, and keywords drive the most conversions
- Access consistent, clear data to prove ROI on all of your campaigns
- Optimize campaigns, ads, and keywords with the highest-value sales
- Align sales and marketing teams
- Optimize the content that resonates most with your customers
- Invest in the campaigns that are working, reduce spend on ones that aren’t
- Deliver exceptional customer experiences
The more you know your customer, their likes, and dislikes, where they’re engaging with your organization, and what’s getting their attention, the better positioned you are to not only drive sales and revenue but also provide exceptional customer experience and build a loyal customer base.
Getting Started with your Marketing Attribution Strategy
Implementing a marketing attribution model should begin with assessing which model will best meet your organization’s goals. Once you choose a model, you should determine the key performance indicators (KPIs) you will use to gauge success. When these are in place, choose a few team members to facilitate this. It’s suggested to have individuals from both marketing and sales involved.
The next step is to determine how you’ll capture the data necessary to feed your particular model. A great place to start is Google Analytics. It’s a go-to for many marketers and offers a few different marketing attribution models within its interface. However, Google Analytics is still limited by the fact that it’s a web analytics tool. Any advertising that happens offline or off your website might be missed entirely.
If you want data from all online and offline marketing efforts included in your modeling, adding call tracking software to the mix is key. When it comes to tracking phone calls and offline interactions, the trail often goes cold for marketers. You’ll get detailed information from all your advertising efforts when you supplement basic marketing attribution with call tracking.
Because the goal of marketing attribution models is to accurately reflect how your advertising is impacting business outcomes, connecting all the dots will make you better positioned to maximize your marketing efforts and consistently drive results.
There are a few basic things to keep in mind when looking at marketing attribution and call tracking software. Be sure the software:
- Offers tracking and attribution for all sources–both online and offline
- Integrates with marketing platforms you already use
- Provides flexible attribution model options
- Meets security and privacy requirements
- Is customizable and can scale with you
- Offers specific features your organization needs
Once you have everything in place, get started tracking and attributing. Look for real-time actionable insights as well as trends over longer periods. And, as with all marketing efforts, continue to test, optimize, and repeat.
If you’re like so many marketers and are still trying to connect the dots in your marketing data and clearly understand your buyer’s journey, multi-touch attribution may be the answer. CallTrackingMetrics helps you get data on exactly which marketing campaigns are working the best so you can increase conversions and drive revenue. Book a Demo today!